- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
RSEM: accurate transcript quantification from RNA-Seq data with or without a reference genome
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
RNA-Seq is revolutionizing the way transcript abundances are measured. A key challenge in transcript quantification from RNA-Seq data is the handling of reads that map to multiple genes or isoforms. This issue is particularly important for quantification with de novo transcriptome assemblies in the absence of sequenced genomes, as it is difficult to determine which transcripts are isoforms of the same gene. A second significant issue is the design of RNA-Seq experiments, in terms of the number of reads, read length, and whether reads come from one or both ends of cDNA fragments.
Results
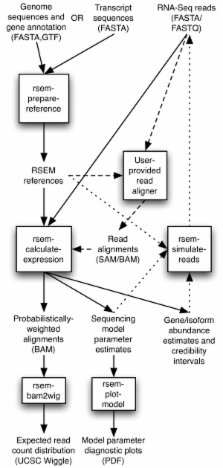
We present RSEM, an user-friendly software package for quantifying gene and isoform abundances from single-end or paired-end RNA-Seq data. RSEM outputs abundance estimates, 95% credibility intervals, and visualization files and can also simulate RNA-Seq data. In contrast to other existing tools, the software does not require a reference genome. Thus, in combination with a de novo transcriptome assembler, RSEM enables accurate transcript quantification for species without sequenced genomes. On simulated and real data sets, RSEM has superior or comparable performance to quantification methods that rely on a reference genome. Taking advantage of RSEM's ability to effectively use ambiguously-mapping reads, we show that accurate gene-level abundance estimates are best obtained with large numbers of short single-end reads. On the other hand, estimates of the relative frequencies of isoforms within single genes may be improved through the use of paired-end reads, depending on the number of possible splice forms for each gene.
Conclusions
RSEM is an accurate and user-friendly software tool for quantifying transcript abundances from RNA-Seq data. As it does not rely on the existence of a reference genome, it is particularly useful for quantification with de novo transcriptome assemblies. In addition, RSEM has enabled valuable guidance for cost-efficient design of quantification experiments with RNA-Seq, which is currently relatively expensive.
Related collections
Most cited references15
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The transcriptional landscape of the yeast genome defined by RNA sequencing.

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Improving RNA-Seq expression estimates by correcting for fragment bias
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found