- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Prognostic factors of 112 elderly patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer
Read this article at
Abstract
Objectives:
In this study we retrospectively analyzed the prognostic factors of patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
Methods:
Clinical data of 112 patients with advanced NSCLC treated in the tumor center of our hospital from January 2016 to December 2017 were analyzed retrospectively, follow up the survival of patients, the effects of gender, age, tumor stage, pathological type, performance status (PS) score, smoking history and treatment on the survival of elderly patients with advanced NSCLC were analyzed.
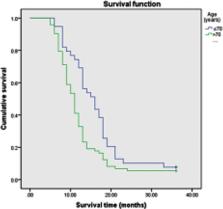
Results: The median survival time was 12.0 months, and the median age was 74 years. The 3-year survival rate after confirmation of advanced lung cancer was 6.25%. Kaplan Meier univariate analysis showed that age, PS score, smoking status and treatment correlated with the prognosis( P<0.05). Cox multivariate analysis showed that age >70 years, PS score>2, smoking and no targeted therapy were independent adverse prognostic factors for elderly patients with advanced NSCLC( P<0.05).
Related collections
Most cited references21
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer: Epidemiology, Screening, Diagnosis, and Treatment
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Systemic Therapy for Locally Advanced and Metastatic Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found