- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Cytopathic bovine viral diarrhea viruses (BVDV): emerging pestiviruses doomed to extinction
Read this article at
Abstract
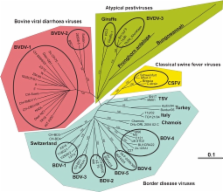
Bovine viral diarrhea virus (BVDV), a Flaviviridae pestivirus, is arguably one of the most widespread cattle pathogens worldwide. Each of its two genotypes has two biotypes, non-cytopathic (ncp) and cytopathic (cp). Only the ncp biotype of BVDV may establish persistent infection in the fetus when infecting a dam early in gestation, a time point which predates maturity of the adaptive immune system. Such fetuses may develop and be born healthy but remain infected for life. Due to this early initiation of fetal infection and to the expression of interferon antagonistic proteins, persistently infected (PI) animals remain immunotolerant to the infecting viral strain. Although only accounting for some 1% of all animals in regions where BVDV is endemic, PI animals ensure the viral persistence in the host population. These animals may, however, develop the fatal mucosal disease, which is characterized by widespread lesions in the gastrointestinal tract. Cp BVD virus, in addition to the persisting ncp biotype, can be isolated from such animals. The cp viruses are characterized by unrestrained genome replication, and their emergence from the persisting ncp ones is due to mutations that are unique in each virus analyzed. They include recombinations with host cell mRNA, gene translocations and duplications, and point mutations. Cytopathic BVD viruses fail to establish chains of infection and are unable to cause persistent infection. Hence, these viruses illustrate a case of “viral emergence to extinction” – irrelevant for BVDV evolution, but fatal for the PI host.
Related collections
Most cited references91
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Classical swine fever virus Npro interacts with interferon regulatory factor 3 and induces its proteasomal degradation.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Identification of a new group of bovine viral diarrhea virus strains associated with severe outbreaks and high mortalities.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found