- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Total Knee Replacement: Subject-Specific Modeling, Finite Element Analysis, and Evaluation of Dynamic Activities
Read this article at
Abstract
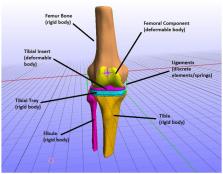
This study presents a semi-automatic framework to create subject-specific total knee replacement finite element models, which can be used to analyze locomotion patterns and evaluate knee dynamics. In recent years, much scientific attention was attracted to pre-clinical optimization of customized total knee replacement operations through computational modeling to minimize post-operational adverse effects. However, the time-consuming and laborious process of developing a subject-specific finite element model poses an obstacle to the latter. One of this work's main goals is to automate the finite element model development process, which speeds up the proposed framework and makes it viable for practical applications. This pipeline's reliability was ratified by developing and validating a subject-specific total knee replacement model based on the 6th SimTK Grand Challenge data set. The model was validated by analyzing contact pressures on the tibial insert in relation to the patient's gait and analysis of tibial contact forces, which were found to be in accordance with the ones provided by the Grand Challenge data set. Subsequently, a sensitivity analysis was carried out to assess the influence of modeling choices on tibial insert's contact pressures and determine possible uncertainties on the models produced by the framework. Parameters, such as the position of ligament origin points, ligament stiffness, reference strain, and implant-bone alignment were used for the sensitivity study. Notably, it was found that changes in the alignment of the femoral component in reference to the knee bones significantly affect the load distribution at the tibiofemoral joint, with an increase of 206.48% to be observed at contact pressures during 5° internal rotation. Overall, the models produced by this pipeline can be further used to optimize and personalize surgery by evaluating the best surgical parameters in a simulated manner before the actual surgery.
Related collections
Most cited references59
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The Chitranjan Ranawat award: is neutral mechanical alignment normal for all patients? The concept of constitutional varus.

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
OpenSim: Simulating musculoskeletal dynamics and neuromuscular control to study human and animal movement
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found