- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) nuclear enriched abundant transcript 1 (NEAT1) regulates fibroblast growth factor receptor substrate 2 (FRS2) by targeting microRNA (miR)-29-3p in hypertrophic scar fibroblasts
Read this article at
ABSTRACT
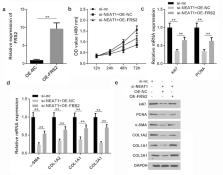
Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) play crucial roles in human diseases. However, the detailed role of lncRNAs in hypertrophic scar fibroblasts (HSFs) is inadequately understood. This study aimed to investigate the potential role of lncRNA nuclear enriched abundant transcript 1 (NEAT1) in hypertrophic scarring. Expression of lncRNAs, miRNAs, and genes were detected by polymerase chain reaction; protein expression was evaluated using western blotting. Cellular function was determined using the CCK-8 assay. The interaction between microRNA (miR)-29-3p and NEAT1 or fibroblast growth factor receptor substrate 2 (FRS2) was verified by luciferase and RNA pull-down assays. The results showed that NEAT1 was overexpressed in the hypertrophic dermis and in HSFs. However, knockdown of NEAT1 suppressed the proliferation and extracellular matrix (ECM) production of HSFs. Moreover, NEAT1 functioned as a competing endogenous RNA to upregulate FRS2 by sponging miR-29-3p. Downregulation of miR-29-3p or overexpression of FRS2 antagonized the effects of NEAT1 knockdown and promoted HSF proliferation and ECM release. In conclusion, NEAT1 knockdown protected against hypertrophic scarring by modulating the miR-29-3p/FRS2 axis, which is a viable target in scar treatment.
Related collections
Most cited references40
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
MicroRNA signatures in human cancers.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found