- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Aging affects the biological activity of fibroblast growth factor (FGF) in gastric epithelial cell, which is partially rescued by uridine
Read this article at
ABSTRACT
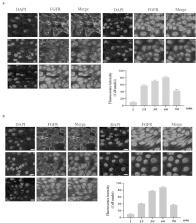
Aging has become an irreversible trend in the world, the health problems caused by aging cannot be ignored. The physiological functions of human body begin to decline with aging, the decline of gastrointestinal function caused by aging is an important problem that needs to be resolved. In this work, we evaluated the anti-aging effect of uridine in the senescent gastric epithelial cell model, and found that the aging level of gastric epithelial cell was significantly down-regulated by uridine treatment, uridine could obviously down-regulate the ratio of the SA-β-gal-positive senescent cells. Furthermore, aging-related marker molecules (such as p16 and p21) were also significantly down-regulated under uridine treatment. Additionally, the levels of inflammation and oxidative stress were also significantly reduced by uridine treatment. Next, our further studies the effect of aging on FGF activity on gastric epithelial cell, and found that FGF/FGFR-mediated signaling pathways were significantly down-regulated. However, uridine treatment can not only alleviate the senescence of gastric epithelial cell, but also can partially restore the sensitivity of FGF signaling. Taken together, the current work indicates that uridine shows a good anti-aging effect, which lays a solid foundation for the related research in this filed.
Graphical abstract
Related collections
Most cited references29
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Crystal structure of a ternary FGF-FGFR-heparin complex reveals a dual role for heparin in FGFR binding and dimerization.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptors (FGFRs): Structures and Small Molecule Inhibitors
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
