- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Sprouts vs. Microgreens as Novel Functional Foods: Variation of Nutritional and Phytochemical Profiles and Their In vitro Bioactive Properties
Read this article at
Abstract
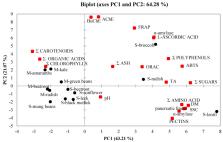
The aim of the study was to analyze potential health-promoting and nutritional components (polyphenols, L-ascorbic acid, carotenoids, chlorophylls, amino acids, organic acid, sugars, ash and pectins) of selected sprouts (radish, lentil, black medick, broccoli, sunflower, leek, beetroot, mung beans) and microgreens (kale, radish, beetroot, green peas, amaranth). Moreover, antioxidant capacity (2,2′-azino-bis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulphonic acid) (ABTS), ferric reducing ability of plasma (FRAP), and oxygen radical absorbance capacity (ORAC)), in vitro anti-diabetic potential (inhibition of α-amylase and α-glucosidase), and anti-obesity (pancreatic lipase) and anti-cholinergic (acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase) activity were evaluated. The results of this study show that sprouts are effective in antioxidant capacity as a result of a high content of polyphenols and L-ascorbic acid. Additionally, sprouts are better sources of amino acids, pectins and sugars than microgreens. Microgreens were characterized by high content of carotenoids and chlorophylls, and organic acid, without any sugars, exhibiting higher anti-diabetic and anti-cholinergic activity than sprouts. Some selected sprouts (broccoli, radish, lentil) and microgreens (radish, amaranths, kale) should be used daily as superfoods or functional food.
Related collections
Most cited references43
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Antioxidant activity applying an improved ABTS radical cation decolorization assay
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The ferric reducing ability of plasma (FRAP) as a measure of "antioxidant power": the FRAP assay.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found