- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
NfiR, a New Regulatory Noncoding RNA (ncRNA), Is Required in Concert with the NfiS ncRNA for Optimal Expression of Nitrogenase Genes in Pseudomonas stutzeri A1501
Read this article at
Abstract
Biological nitrogen fixation is an energy-expensive process requiring the hydrolysis of 16 ATPs. Consequently, the expression of nif genes is highly regulated at both transcriptional and posttranscriptional levels through complex regulatory networks. Global regulation involves a number of regulatory proteins, such as the nif-specific activator NifA and the global nitrogen regulator NtrC, as well as various regulatory ncRNAs. We show that the two P. stutzeri ncRNAs, namely NfiS and NfiR (for nitrogen fixation condition- inducible nc RNA), optimize nitrogen fixation and environmental stress responses. NfiS and NfiR respond differently to various environmental signals and differ in their secondary structures. In addition, the two ncRNAs target the mRNAs of nifK and nifD, respectively. Such ncRNA-based posttranscriptional regulation of nitrogenase expression might be an evolved survival strategy, particularly in nitrogen-limiting environments. This study not only highlights the significant roles of regulatory ncRNAs in the coordination and fine tuning of various physiological processes but also provides a new paradigm for posttranscriptional regulation in nitrogen-fixing bacteria.
ABSTRACT
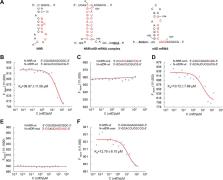
Expression of nitrogenase genes ( nifHDK) is strictly regulated at both transcriptional and posttranscriptional levels. Efficient nitrogenase activity requires maintaining sufficient levels of nif mRNAs, yet the underlying mechanism is not fully understood due to its complexity. We have previously shown that a novel regulatory noncoding RNA (ncRNA), NfiS, optimizes nitrogen fixation through targeting nifK mRNA in Pseudomonas stutzeri A1501. Here, we report the identification and characterization of a second ncRNA inducible under nitrogen fixation conditions (nitrogen-free and microaerobic conditions), termed NfiR (for nitrogen fixation condition- inducible nc RNA), the expression of which is dependent on two global regulators, NtrC and Hfq. Comparative phenotypic and proteomic analyses of an nfiR mutant identify a role of NfiR in regulating the expression of nitrogenase genes. Further microscale thermophoresis and genetic complementation showed that an 11-nucleotide (nt) sequence in the stem-loop structure of NfiR (nucleotides 12 to 22) pairs with its counterpart in the coding region of nifD mRNA (nucleotides 1194 to 1207) by eight nucleotides. Significantly, deletion of nfiR caused a 60% reduction of nitrogenase activity, and the half-life of nifD mRNA was reduced from 20 min for the wild type to 15 min for the Δ nfiR mutant. With regard to nitrogenase activity and stability of the nifD and nifK transcripts, phenotypes were more severe for the double deletion mutant lacking nfiR and nfiS, suggesting that NfiR, in concert with NfiS, optimizes nitrogenase production at the posttranscriptional level.
IMPORTANCE Biological nitrogen fixation is an energy-expensive process requiring the hydrolysis of 16 ATPs. Consequently, the expression of nif genes is highly regulated at both transcriptional and posttranscriptional levels through complex regulatory networks. Global regulation involves a number of regulatory proteins, such as the nif-specific activator NifA and the global nitrogen regulator NtrC, as well as various regulatory ncRNAs. We show that the two P. stutzeri ncRNAs, namely NfiS and NfiR (for nitrogen fixation condition- inducible nc RNA), optimize nitrogen fixation and environmental stress responses. NfiS and NfiR respond differently to various environmental signals and differ in their secondary structures. In addition, the two ncRNAs target the mRNAs of nifK and nifD, respectively. Such ncRNA-based posttranscriptional regulation of nitrogenase expression might be an evolved survival strategy, particularly in nitrogen-limiting environments. This study not only highlights the significant roles of regulatory ncRNAs in the coordination and fine tuning of various physiological processes but also provides a new paradigm for posttranscriptional regulation in nitrogen-fixing bacteria.
Related collections
Most cited references39
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Regulatory RNAs in bacteria.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Pseudomonas genomes: diverse and adaptable.
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found