- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Accelerated discovery of superoxide-dismutase nanozymes via high-throughput computational screening
Read this article at
Abstract
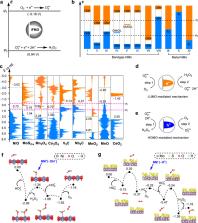
The activity of nanomaterials (NMs) in catalytically scavenging superoxide anions mimics that of superoxide dismutase (SOD). Although dozens of NMs have been demonstrated to possess such activity, the underlying principles are unclear, hindering the discovery of NMs as the novel SOD mimics. In this work, we use density functional theory calculations to study the thermodynamics and kinetics of the catalytic processes, and we develop two principles, namely, an energy level principle and an adsorption energy principle, for the activity. The first principle quantitatively describes the role of the intermediate frontier molecular orbital in transferring electrons for catalysis. The second one quantitatively describes the competition between the desired catalytic reaction and undesired side reactions. The ability of the principles to predict the SOD-like activities of metal-organic frameworks were verified by experiments. Both principles can be easily implemented in computer programs to computationally screen NMs with the intrinsic SOD-like activity.
Abstract
A general predicting theory for superoxide-dismutase mimicking nanomaterials is currently lacking. The present manuscript reports a density functional theory study on the superoxides dismutase-like activity of nanomaterials based on their electronic band structures and surface adsorption energies.
Related collections
Most cited references67
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Generalized Gradient Approximation Made Simple
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found