- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Engineering nano-drug biointerface to overcome biological barriers toward precision drug delivery
Read this article at
Abstract
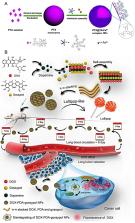
The rapid advancement of nanomedicine and nanoparticle (NP) materials presents novel solutions potentially capable of revolutionizing health care by improving efficacy, bioavailability, drug targeting, and safety. NPs are intriguing when considering medical applications because of their essential and unique qualities, including a significantly higher surface to mass ratio, quantum properties, and the potential to adsorb and transport drugs and other compounds. However, NPs must overcome or navigate several biological barriers of the human body to successfully deliver drugs at precise locations. Engineering the drug carrier biointerface can help overcome the main biological barriers and optimize the drug delivery in a more personalized manner. This review discusses the significant heterogeneous biological delivery barriers and how biointerface engineering can promote drug carriers to prevail over hurdles and navigate in a more personalized manner, thus ushering in the era of Precision Medicine. We also summarize the nanomedicines' current advantages and disadvantages in drug administration, from natural/synthetic sources to clinical applications. Additionally, we explore the innovative NP designs used in both non-personalized and customized applications as well as how they can attain a precise therapeutic strategy.
Related collections
Most cited references219
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Analysis of nanoparticle delivery to tumours

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found