- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Circular RNAs: A novel type of non-coding RNA and their potential implications in antiviral immunity
Read this article at
Abstract
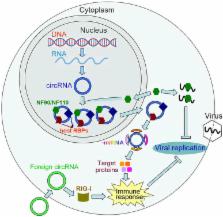
Circular RNAs (circRNAs), a novel type of non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs), are ubiquitously expressed in eukaryotic cells during post-transcriptional processes. Unlike linear RNAs, circRNAs form covalent-closed continuous loops without 5' to 3' polarities and poly (A) tails. With advances in high-throughput sequencing technology, numerous circRNAs have been identified in plants, animals and humans. Notably, circRNAs display cell-type, tissue-type and developmental-stage specific expression patterns in eukaryotic transcriptome, which reveals their significant regulatory functions in gene expression. More importantly, circRNAs serve as microRNA (miRNA) sponges and crucial regulators of gene expression. Additionally, circRNAs modulate pre-mRNA alternative splicing and possess protein-coding capacity. CircRNAs exhibit altered expression under pathological conditions and are strongly associated with the development of various human diseases. Interestingly, circRNAs can also induce antiviral immune responses. A recent study found that the delivery of circRNAs generated in vitro activates RIG-I-mediated innate immune responses and provides protection against viral infection. The antiviral dsRNA-binding proteins, NF90/NF110, act as key regulators in circRNA biogenesis. NF90/NF110 are also functional in inhibiting viral replication through binding to viral mRNAs. In this review, we provide a comprehensive overview on the classification, biogenesis and functions of circRNAs. We also discuss the critical role of circRNAs in eliciting antiviral immunity, providing evidence for the potential implications of circRNAs in antiviral therapies.
Related collections
Most cited references57
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The transcriptional landscape of the mammalian genome.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Roles for microRNAs in conferring robustness to biological processes.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found