- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
The Pattern of Mandibular Third Molar Impaction and Assessment of Surgery Difficulty: A Retrospective Study of Radiographs in East Baltic Population
Read this article at
Abstract
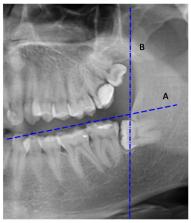
Classifications of impacted teeth allow defining the type and degree of retention, as well as assessing the degree of difficulty of the procedure. The aim of this study was to conduct retrospective analysis of the degree of retention and difficulty in the surgical removal of impacted mandibular third molars in the clinical material of the Department of Oral Surgery in 2013–2018. This study included 1585 dental panoramic radiographs of patients of the Department of Oral Surgery, who reported in 2013–2018, in order to perform surgical removal of the impacted mandibular third molar. Based on dental panoramic radiographs, the degree of retention was determined based on classifications according to Winter, according to Pell and Gregory, according to Tetsch and Wagner, and according to Asanami and Kasazaki. The difficulty of the procedure was also assessed based on the Pederson index. The most common types of lower wisdom tooth impaction are as follows: in Winter’s classification, mesial-angular impaction; in Tetsch and Wagner’s classification, oblique medial-angular impaction; in Pell and Gregory’s classification, impaction grade 2A; and in Asanami and Kasazaki’s classification, 3A and anterior inclination. In most cases of surgical removal of an impacted tooth, the anticipated difficulty of the procedure was rated as very difficult.
Related collections
Most cited references47
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Extraction of impacted mandibular third molars: postoperative complications and their risk factors.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Prevalence of impacted teeth and associated pathologies--a radiographic study of the Hong Kong Chinese population.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found