- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Colorectal Cancer Screening: a Systematic Review
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
After the World Health Organization (WHO) announcing about global pandemic of COVID-19 in March 2020 and relocation of health care resources for controlling this infection, cancer screening programs especially colorectal cancer (CRC) have been suspended in many countries. According to GLOBOCAN 2020 data, CRC is the third prevalent and second deadliest cancer in the world. So, early detection through screening is essential to reduce the mortality associated with this cancer. The present study was designed to investigate the impact of COVID-19 pandemic on colorectal cancer screening.
Methods and Materials
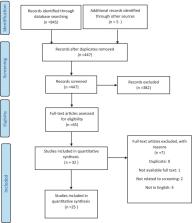
A comprehensive search performed on June 2021 in various databases, including Medline, Web of Science, and Scopus. Keywords such as “Early Detection,” “Cancer,” “Cancer Screening,” “Cancer Screening Tests,” “Coronavirus Disease-19,” “COVID 19,” “Coronavirus Disease,” “SARS-CoV-2 Infection,” “SARS-CoV-2,” “2019-nCoV,” “coronavirus, 2019 Novel,” “SARS COV 2 Virus,” “Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2,” “COVID-19,” “COVID-19, Coronavirus Disease 19,” “SARS Coronavirus 2”,“Colorectal neoplasm” and “Colorectal Cancer“ were used individually or in combination to search. All articles were entered into Endnote X7 software that remove duplicates. Then, studies were first selected by title and then by abstract and at the end full texts were investigated.
Results
Of the 850 identified studies, 25 were identified as eligible. The results of studies show that in general, colorectal cancer screening has decreased from 28 to 100% in different countries and at different times after the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic. During this period, only 2 to 2.5% of hospitals and screening centers with 100% capacity continued to operate, and more than 77% of them limited their activities to less than 10% of their normal capacity. Also, completion of colonoscopies requiring examination showed a decrease of 65.7%, surveillance colonoscopy showed a decrease of 44.6 to 79%, prescription colonoscopy decreased 60 to 81%, and referrals to colonoscopy showed a 43% decline. However, emergency colonoscopy shows a 2 to 9% increase. The use of the Fecal immunochemical test (FIT) test is also generally declining but is increasing in areas used as a colonoscopy alternative.
Conclusions
Considering that the reduction in colorectal cancer screening following COVID-19 pandemic is due to the restrictions imposed for the high prevalence of COVID-19 disease and the lack of referrals due to the fear of developing COVID-19 infection; compensating for the decline and preventing the continuation of this decreasing trend requires serious and effective interventions to maintain the capacity of screening services during the COVID-19 crisis, increase the capacity of screening centers during the lifting of restrictions and reduce fear in the public.
Related collections
Most cited references25
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Early Transmission Dynamics in Wuhan, China, of Novel Coronavirus–Infected Pneumonia

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on cancer deaths due to delays in diagnosis in England, UK: a national, population-based, modelling study
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
