- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Medical tourism and policy implications for health systems: a conceptual framework from a comparative study of Thailand, Singapore and Malaysia
Read this article at
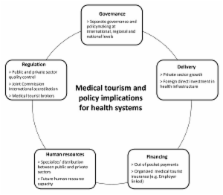
Abstract
Medical tourism is a growing phenomenon with policy implications for health systems, particularly of destination countries. Private actors and governments in Southeast Asia are promoting the medical tourist industry, but the potential impact on health systems, particularly in terms of equity in access and availability for local consumers, is unclear. This article presents a conceptual framework that outlines the policy implications of medical tourism's growth for health systems, drawing on the cases of Thailand, Singapore and Malaysia, three regional hubs for medical tourism, via an extensive review of academic and grey literature. Variables for further analysis of the potential impact of medical tourism on health systems are also identified. The framework can provide a basis for empirical, in country studies weighing the benefits and disadvantages of medical tourism for health systems. The policy implications described are of particular relevance for policymakers and industry practitioners in other Southeast Asian countries with similar health systems where governments have expressed interest in facilitating the growth of the medical tourist industry. This article calls for a universal definition of medical tourism and medical tourists to be enunciated, as well as concerted data collection efforts, to be undertaken prior to any meaningful empirical analysis of medical tourism's impact on health systems.
Related collections
Most cited references24
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
An assessment of interactions between global health initiatives and country health systems.
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Medical tourism: Sea, sun, sand and … surgery
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found