- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
The Administration of Levodopa in a Patient With Parkinson’s Disease Using a Novel Maxillofacial Route: A First-in-Human Report
Read this article at
Abstract
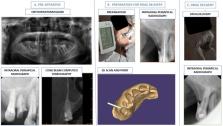
Parkinson's disease is characterized by the loss of nigrostriatal dopaminergic neurons in the brain. Dopamine cannot be administered systemically because it does not cross the blood-brain barrier. Oral levodopa remains the gold standard to date. Currently, for patients who show a poor response to oral levodopa and for those who cannot take it orally, the alternate routes available are inhalation and continuous administration via intestinal and subcutaneous routes. In this report, a novel maxillofacial route was used for the first time in the world to administer levodopa to a Parkinson's patient. Furthermore, the efficacy of maxillofacial administration was compared with the oral route of administration.
Related collections
Most cited references17
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Parkinson disease-associated cognitive impairment
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Long term motor complications of levodopa: clinical features, mechanisms, and management strategies.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found