- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Characteristics of behavioural addiction in Parkinson’s disease patients with self-reported impulse control disorder and controls matched for levodopa equivalent dose: a matched case–control study
Read this article at
Abstract
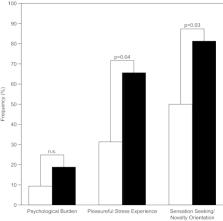
Impulse control disorders (ICD) in Parkinson’s disease (PD) frequently occur, not always as a direct consequence of dopaminergic medication. This study investigated premorbid personality traits and behavioural characteristics in non-demented PD patients with self-reported symptoms of ICD (PD-srICD). From a total of 200 non-demented PD patients who filled out questionnaires assessing symptoms and severity of ICD, those were classified as PD-srICD ( n = 32) who reported current occurrence of at least one compulsive behaviour (gambling, sexual behaviour, buying behaviour, or eating). As a control group, 32 patients with no self-reported ICD symptoms were matched for levodopa equivalent daily dose. The demographic, clinical, and premorbid personality profiles were compared between both groups. Frequency of psychological characteristics indicating substance use disorder was evaluated in patients with PD-srICD. Patients with PD-srICD were more frequently male, younger at examination, had earlier PD onset, more depression, higher non-motor burden, less quality of life ( p < 0.05, respectively), and more frequently reported premorbid sensation seeking/novelty orientation ( p = 0.03) and joyful experience of stress ( p = 0.04) than patients in the control group. Of patients with PD-srICD, 90.6% reported at least one behavioural characteristic of substance use disorder, most frequently positive expectations following ICD behaviour and illusional beliefs about its behavioural control. Signs of addiction were common among patients with PD-srICD. Therefore, the profile of psychological characteristics in patients with PD-srICD resembled that of patients with substance use disorder. It can be concluded that dopamine replacement therapy (DRT) alone does not account for PD-srICD and that thorough psychological diagnostics are recommended.
Related collections
Most cited references48
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Research electronic data capture (REDCap)--a metadata-driven methodology and workflow process for providing translational research informatics support.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The Montreal Cognitive Assessment, MoCA: a brief screening tool for mild cognitive impairment.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found