- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
The association between mean platelet volume and inflammation in geriatric patients with emergency hypertension
Read this article at
Abstract
Objectives
We aimed to investigate the role of inflammation parameters and platelet activation in geriatric patients with hypertension. Therefore, we compared the levels of those parameters in patients with hypertensive urgency and emergency. We also investigated the potential relationship between those parameters.
Methods
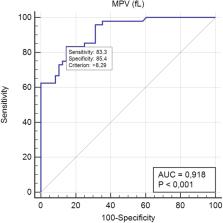
Ninety-six hypertensive (HT) patients (aged > 60) were included in the study in two groups: HT emergency (N = 48, group 1) and HT urgency (N = 48, group 2). Mean platelet volume (MPV), neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and high-sensitive C reactive protein (hs-CRP) were compared between those groups. Optimum cut-off levels of each parameter were determined by the use of Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis. Pearson correlation test was used to examine the relationship between variables.
Results
The mean MPV and hs-CRP levels were significantly higher in patients with HT emergencies (both P < 0.001). Mean NLR was also significantly different between the two groups (P = 0.011). Pearson correlation analysis revealed a positive but weak correlation between the MPV and NLR (r = 0.245, P = 0.016), the hs-CRP level (r = 0.394, P < 0.001), and the WBC count (r = 0.362, P < 0.001).
Related collections
Most cited references15
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Mean platelet volume as an indicator of platelet activation: methodological issues.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Mean platelet volume and coronary artery disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found