- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Protein Polymer-Based Nanoparticles: Fabrication and Medical Applications
Read this article at
Abstract
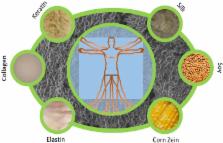
Nanoparticles are particles that range in size from about 1–1000 nanometers in diameter, about one thousand times smaller than the average cell in a human body. Their small size, flexible fabrication, and high surface-area-to-volume ratio make them ideal systems for drug delivery. Nanoparticles can be made from a variety of materials including metals, polysaccharides, and proteins. Biological protein-based nanoparticles such as silk, keratin, collagen, elastin, corn zein, and soy protein-based nanoparticles are advantageous in having biodegradability, bioavailability, and relatively low cost. Many protein nanoparticles are easy to process and can be modified to achieve desired specifications such as size, morphology, and weight. Protein nanoparticles are used in a variety of settings and are replacing many materials that are not biocompatible and have a negative impact on the environment. Here we attempt to review the literature pertaining to protein-based nanoparticles with a focus on their application in drug delivery and biomedical fields. Additional detail on governing nanoparticle parameters, specific protein nanoparticle applications, and fabrication methods are also provided.
Related collections
Most cited references115
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Nanoparticle-based targeted drug delivery.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Nanoparticle polymer composites: where two small worlds meet.
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found