- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Critical Appraisal of the Concept Frailty: Rating of Frailty in Elderly People has Weak Scientific Basis and should not be Used for Managing Individual Patients
Read this article at
Abstract
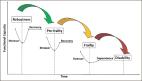
The concept frail elderly has been used to highlight the biological, rather than chronological, age. International and national bodies recommend that individuals over age 70 who visit healthcare facilities should be screened for frailty. There are important objections to the concept. Diagnostics: ‘Frailty’ is used for several completely different types of health problems. There are no useful biomarkers, but more than 60 different published rating methods for frailty, where different methods provide very different prevalence of frailty and also do not identify the same groups of elderly people. There is significant overlap between Clinical Frailty Scale- scores and activity of daily living (ADL)-scores. There is no gold standard method against which published frailty rating scales can be validated. It is unclear when, where and how often screening for frailty should occur in healthcare. Treatment: The evidence for treatment of frailty is very weak. A recent systematic overview found that the 21 included randomised, controlled studies (RCTs) were very heterogeneous as regards inclusion/exclusion criteria, how the condition of frailty was defined, what treatment was given and what health outcomes were assessed. In addition, there are often problems with the quality of the studies. The lack of a clear definition and evidence-based treatment of frailty means that it is inappropriate to introduce assessments of frailty in individual elderly patients in health care
Related collections
Most cited references25
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
A global clinical measure of fitness and frailty in elderly people.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Physical Frailty: ICFSR International Clinical Practice Guidelines for Identification and Management
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found