- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
In situ generation of turbostratic nickel hydroxide as a nanozyme for salivary glucose sensor†

Read this article at
Abstract
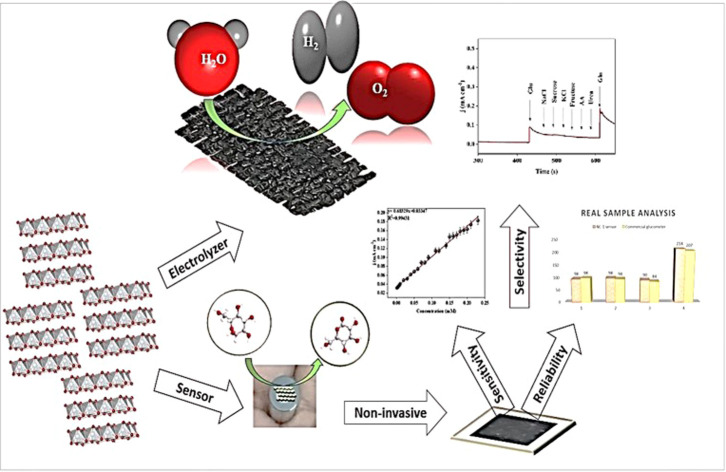
Among the 3d-transition metal hydroxide series, nickel hydroxide is a well-studied electroactive catalyst. In particular, nickel hydroxide and its composite materials are well-suited for non-enzymatic glucose sensing. The electrocatalytic efficiency of nickel hydroxide is attributed to the thickness or to be precise, the thinness of the electroactive layer. Herein, we have successfully prepared metallic nickel@nickel hydroxide nanosheets through a straightforward one-pot solvothermal method. We were able to electrochemically generate a highly sensitive α-Ni(OH) 2 on the nanosheets. The dynamic generation and synergy between α- and β-Ni(OH) 2, imparts a glucose oxidase enzyme-like ability to the catalyst. Our proposed nickel nanozyme exhibits a good sensitivity of 683 μA mM −1 cm −2 for glucose. The sensor operates in the range of 0.001–3.1 mM, with a lower limit of detection (LOD) of 9.1 μM and exhibits a response time of ≈00.1 s. Nickel-nanozyme demonstrated better selectivity for glucose in the presence of interfering compounds. Notably, the sensor does not suffer from an interfering oxygen evolution reaction. This greatly improves sensitivity in glucose detection in lower concentrations making the sensor viable to measure salivary glucose levels. In this study, we demonstrate that our sensor can detect glucose in human saliva. The real sample analysis was carried out with saliva samples from three healthy human volunteers and one prediabetic volunteer. Our proposed sensor measurements show excellent agreement with calculated salivary glucose levels with 98% accuracy in sensing glucose in real saliva samples.
Abstract
Turbostratic nickel hydroxide as a salivary glucose sensor.