- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Neuroinflammatory mechanisms of blood-brain barrier damage in ischemic stroke
February 2019
February 2019
Read this article at
There is no author summary for this article yet. Authors can add summaries to their articles on ScienceOpen to make them more accessible to a non-specialist audience.
Abstract
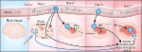
As part of the neurovascular unit, the blood-brain barrier (BBB) is a unique, dynamic
regulatory boundary that limits and regulates the exchange of molecules, ions, and
cells between the blood and the central nervous system. Disruption of the BBB plays
an important role in the development of neurological dysfunction in ischemic stroke.
Blood-borne substances and cells have restricted access to the brain due to the presence
of tight junctions between the endothelial cells of the BBB. Following stroke, there
is loss of BBB tight junction integrity, leading to increased paracellular permeability,
which results in vasogenic edema, hemorrhagic transformation, and increased mortality.
Thus, understanding principal mediators and molecular mechanisms involved in BBB disruption
is critical for the development of novel therapeutics to treat ischemic stroke. This
review discusses the current knowledge of how neuroinflammation contributes to BBB
damage in ischemic stroke. Specifically, we provide an updated overview of the role
of cytokines, chemokines, oxidative and nitrosative stress, adhesion molecules, matrix
metalloproteinases, and vascular endothelial growth factor as well as the role of
different cell types in the regulation of BBB permeability in ischemic stroke.
Related collections
Most cited references203
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Inflammatory mechanisms in ischemic stroke: therapeutic approaches
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
