- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Genome-wide identification of genes critical for in vivo fitness of multi-drug resistant porcine extraintestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli by transposon-directed insertion site sequencing using a mouse infection model
Read this article at
ABSTRACT
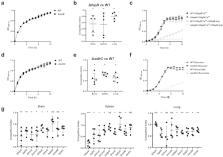
Extraintestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli (ExPEC) is an important zoonotic pathogen. Recently, ExPEC has been reported to be an emerging problem in pig farming. However, the mechanism of pathogenicity of porcine ExPEC remains to be revealed. In this study, we constructed a transposon (Tn) mutagenesis library covering Tn insertion in over 72% of the chromosome-encoded genes of a virulent and multi-drug resistant porcine ExPEC strain PCN033. By using a mouse infection model, a transposon-directed insertion site sequencing (TraDIS) assay was performed to identify in vivo fitness factors. By comparing the Tn insertion frequencies between the input Tn library and the recovered library from different organs, 64 genes were identified to be involved in fitness during systemic infection. 15 genes were selected and individual gene deletion mutants were constructed. The in vivo fitness was evaluated by using a competitive infection assay. Among them, Δ fimG was significantly outcompeted by the WT strain in vivo and showed defective adhesion to host cells. rfa which was involved in lipopolysaccharide biosynthesis was shown to be critical for in vivo fitness which may have resulted from its role in the resistance to serum killing. In addition, several metabolic genes including fepB, sdhC, fepG, gltS, dcuA, ccmH, ddpD, narU, glpD, malM, and yabL and two regulatory genes metJ and baeS were shown as important determinants of in vivo fitness of porcine ExPEC. Collectively, this study performed a genome-wide screening for in vivo fitness factors which will be important for understanding the pathogenicity of porcine ExPEC.
Related collections
Most cited references101

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Trimmomatic: a flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found