- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Choline metabolism reprogramming mediates an immunosuppressive microenvironment in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) by promoting tumor-associated macrophage functional polarization and endothelial cell proliferation
Read this article at
Abstract
Introduction
Lung cancer is a prevalent malignancy globally, and immunotherapy has revolutionized its treatment. However, resistance to immunotherapy remains a challenge. Abnormal cholinesterase (ChE) activity and choline metabolism are associated with tumor oncogenesis, progression, and poor prognosis in multiple cancers. Yet, the precise mechanism underlying the relationship between ChE, choline metabolism and tumor immune microenvironment in lung cancer, and the response and resistance of immunotherapy still unclear.
Methods
Firstly, 277 advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients receiving first-line immunotherapy in Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center were enrolled in the study. Pretreatment and the alteration of ChE after 2 courses of immunotherapy and survival outcomes were collected. Kaplan–Meier survival and cox regression analysis were performed, and nomogram was conducted to identify the prognostic and predicted values. Secondly, choline metabolism-related genes were screened using Cox regression, and a prognostic model was constructed. Functional enrichment analysis and immune microenvironment analysis were also conducted. Lastly, to gain further insights into potential mechanisms, single-cell analysis was performed.
Results
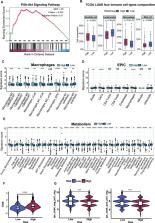
Firstly, baseline high level ChE and the elevation of ChE after immunotherapy were significantly associated with better survival outcomes for advanced NSCLC. Constructed nomogram based on the significant variables from the multivariate Cox analysis performed well in discrimination and calibration. Secondly, 4 choline metabolism-related genes (MTHFD1, PDGFB, PIK3R3, CHKB) were screened and developed a risk signature that was found to be related to a poorer prognosis. Further analysis revealed that the choline metabolism-related genes signature was associated with immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment, immune escape and metabolic reprogramming. scRNA-seq showed that MTHFD1 was specifically distributed in tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs), mediating the differentiation and immunosuppressive functions of macrophages, which may potentially impact endothelial cell proliferation and tumor angiogenesis.
Conclusion
Our study highlights the discovery of ChE as a prognostic marker in advanced NSCLC, suggesting its potential for identifying patients who may benefit from immunotherapy. Additionally, we developed a prognostic signature based on choline metabolism-related genes, revealing the correlation with the immunosuppressive microenvironment and uncovering the role of MTHFD1 in macrophage differentiation and endothelial cell proliferation, providing insights into the intricate workings of choline metabolism in NSCLC pathogenesis.
Related collections
Most cited references54
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found