- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Efficient Vaccine Distribution Based on a Hybrid Compartmental Model
Read this article at
Abstract
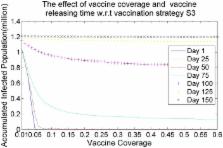
To effectively and efficiently reduce the morbidity and mortality that may be caused by outbreaks of emerging infectious diseases, it is very important for public health agencies to make informed decisions for controlling the spread of the disease. Such decisions must incorporate various kinds of intervention strategies, such as vaccinations, school closures and border restrictions. Recently, researchers have paid increased attention to searching for effective vaccine distribution strategies for reducing the effects of pandemic outbreaks when resources are limited. Most of the existing research work has been focused on how to design an effective age-structured epidemic model and to select a suitable vaccine distribution strategy to prevent the propagation of an infectious virus. Models that evaluate age structure effects are common, but models that additionally evaluate geographical effects are less common. In this paper, we propose a new SEIR (susceptible—exposed—infectious šC recovered) model, named the hybrid SEIR-V model (HSEIR-V), which considers not only the dynamics of infection prevalence in several age-specific host populations, but also seeks to characterize the dynamics by which a virus spreads in various geographic districts. Several vaccination strategies such as different kinds of vaccine coverage, different vaccine releasing times and different vaccine deployment methods are incorporated into the HSEIR-V compartmental model. We also design four hybrid vaccination distribution strategies (based on population size, contact pattern matrix, infection rate and infectious risk) for controlling the spread of viral infections. Based on data from the 2009–2010 H1N1 influenza epidemic, we evaluate the effectiveness of our proposed HSEIR-V model and study the effects of different types of human behaviour in responding to epidemics.
Related collections
Most cited references43
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Emergence and pandemic potential of swine-origin H1N1 influenza virus.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Optimizing influenza vaccine distribution.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found