- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Nasal asymmetry changes during growth and development in 6‐ to 12‐year‐old children with repaired unilateral cleft lip and palate: A 3D computed tomography analysis
Read this article at
Abstract
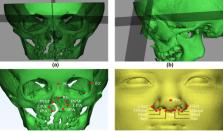
Repaired unilateral cleft lip and palate (UCLP) is often accompanied by the deformity and asymmetry of the nasal region. Three‐dimensional analysis was performed to investigate the relationship between nasal soft‐ and hard‐tissue asymmetries, as well as the changes in nasal asymmetry with age, among children with repaired UCLP (age: 6–12 years). Forty‐seven patients were included in this study. Their computed tomography records were retrieved for analysis of the 3D asymmetry of 10 landmarks of the nasal soft and hard tissues. We observed that asymmetry was more severe in nasal hard tissues than in soft tissues, particularly in the sagittal dimension. Compared with patients aged 6–9 years old, patients aged 10 to 12 years old had significantly increased vertical asymmetry at the base of the alar groove (Gbase, p = 0.027) and the lateral point of the piriform aperture (LPA), ( p < 0.001). The correlation between the LPA and the alar region was weak to moderate ( r = 0.290 to 0.488). In conclusion, we found no evidence of growth and development in nasal hard‐tissue asymmetry among 6‐ to 12‐year‐old children with repaired UCLP, except for the vertical dimension. Nasal soft tissue exhibited a more preferable symmetry than hard tissue, and this could be attributed to the compensatory growth of nasal soft tissue, particularly in the vertical and sagittal dimensions. The weak to moderate correlations between nasal soft‐tissue asymmetry and hard‐tissue asymmetry were observed in the three dimensions. Surgeons should consider these factors when repositioning the nasal alar and controlling the size of the nostrils.
Abstract
Computed tomography records of forty‐seven 6‐ to 12‐year‐old children with repaired unilateral cleft lip and palate were retrieved. The nasal soft‐ and hard‐tissue asymmetries were investigated. We found no evidence of growth and development in the nasal hard‐tissue asymmetry, except for the vertical dimension. Nasal soft tissue exhibited a more preferable symmetry than hard tissue, and this could be attributed to the compensatory growth of nasal soft tissue, particularly in the vertical and sagittal dimensions. The weak to moderate correlations between nasal soft‐tissue asymmetry and hard‐tissue asymmetry were observed in the three dimensions.
Related collections
Most cited references34
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
G*Power 3: A flexible statistical power analysis program for the social, behavioral, and biomedical sciences
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Cleft lip and palate
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
