- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Clinical parameters among patients in Japan with anemia and non-dialysis-dependent chronic kidney disease with and without diabetes mellitus who received roxadustat
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
Roxadustat is an oral hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor for treating anemia of chronic kidney disease (CKD). This post hoc analysis of a Japanese, open-label, partially randomized, phase 3 study in patients with non-dialysis-dependent (NDD) CKD evaluated disease state–related parameters among patients with and without diabetes mellitus who received roxadustat. In the 1517-CL-0310 study (NCT02988973), roxadustat was noninferior to darbepoetin alfa for change in average hemoglobin levels at Weeks 18–24 from baseline who received roxadustat.
Methods
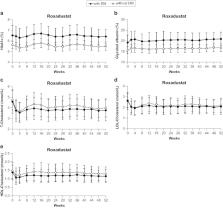
Patients enrolled in the 1517-CL-0310 study who received roxadustat were included in this post hoc analysis. Hematologic (hemoglobin, reticulocyte/erythrocyte ratio, mean corpuscular volume [MCV], and mean corpuscular hemoglobin [MCH]), iron-related (ferritin, total iron-binding capacity, transferrin, ceruloplasmin, and hepcidin), metabolic (HbA1c, glycated albumin, total cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol), and renal (eGFR) parameters were summarized descriptively by visit through Week 52.
Results
Among 201 included patients, 105 (52.2%) and 96 (47.8%) were in the Diabetes and No Diabetes subgroups, respectively. There were no clinically meaningful differences through Week 52 for most hematologic, iron-related, metabolic, or renal parameters between patients in the Diabetes and No Diabetes subgroups. MCV and MCH remained lower and HbA1c and glycated albumin remained higher in patients in the Diabetes subgroup through Week 52. Both subgroups experienced a similar benefit from roxadustat in maintaining hemoglobin levels in the target range of 10–12 g/dL.
Related collections
Most cited references35
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
HIF-1-mediated expression of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase: a metabolic switch required for cellular adaptation to hypoxia.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Mechanisms of anemia in CKD.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found