- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Comparison of the effects of doula supportive care and acupressure at the BL32 point on the mother's anxiety level and delivery outcome
Read this article at
Abstract
Background:
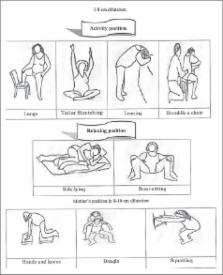
Natural delivery is distressing and the mother's severe pain and anxiety in this condition can have negative impacts on the fetus, mother, and the delivery process. Yet, pain and anxiety can be reduced by supporting the mother by a doula. Thus, the present study aims to compare the effects of doula supportive care and acupressure at the BL32 point on the mother's anxiety level and delivery outcome.
Materials and Methods:
The present clinical trial was conducted on 150 pregnant women who had referred to the Shoushtari Hospital, Shiraz, Iran for delivery in 2012. The subjects were randomly divided into two intervention groups (supportive care and acupressure) and a control group (hospital routine care). The mothers’ anxiety score was assessed before and after the intervention, using the Spielberger questionnaire. The delivery outcomes were evaluated, as well. Subsequently, the data were entered into the SPSS statistical software (Ver. 16) and analyzed using the analysis of variance (ANOVA), Chi-square test, correlation coefficient, and logistic regression analysis.
Results:
After the intervention, the highest and lowest mean scores of the state and trait anxieties were compared with the control and the supportive care groups, respectively, and the difference was statistically significant ( P < 0.001). A significant relationship was found between the labor length and mother's anxiety score after the intervention in the supportive care ( P <</i> 0.001) and the control group ( P = 0.006). However, this relationship was not significant in the acupressure group ( P = 0.425). Also, a significant difference was observed among the three groups regarding the mothers’ anxiety level ( P = 0.009).
Conclusions:
The study results showed that doula supportive care and acupressure at the BL32 point reduced the mother's anxiety as well as the labor length. Therefore, non-pharmacological methods are recommended to be used during labor for improving birth outcomes and creating a positive birth experience.
Related collections
Most cited references49
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Association between maternal anxiety in pregnancy and increased uterine artery resistance index: cohort based study.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
WHO Standard Acupuncture Point Locations
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found