- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Vaginal Hysterectomy at the Time of Total Colpocleisis: A Single-Center Experience
Read this article at
Abstract
Objective: This study aims to evaluate the five-year experience of a single center regarding the total colpocleisis procedure.
Methods: This is a retrospective review of 24 women who underwent total colpocleisis at the study center between January 2017 and January 2023. Every participant was informed about this study, and written consent was obtained from each participant who then took Pelvic Floor Distress Inventory-20 (PFDI-20), Body Appreciation Scale-2 (BAS-2) and Decision Regret Scale (DRS) questionnaires consecutively.
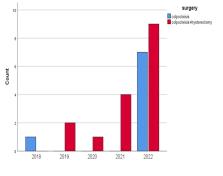
Results: Eight patients (33.3%) underwent total colpocleisis, whereas 16 patients (66.7%) had concomitant colpocleisis and vaginal hysterectomy. The number of total colpocleisis cases did not change significantly with respect to the past years (p=0.117). The patients who underwent total colpocleisis and the patients who had concurrent colpocleisis and hysterectomy were statistically similar with respect to age, gravidity, chronic disease, blood group, American Society of Anesthesiologists classification, anesthesia type, surgery timing and preoperative and postoperative hemoglobin values (p>0.05 for all). Operative time was significantly shorter in patients who had colpocleisis alone (p=0.001). Both patient groups were also statistically similar in aspects of blood loss, transfusion need, hospital stay, postoperative complications and follow-up time as well as PFDI-20, BAS-2 and DRS scores (p>0.05 for all). Endometrial atrophy (56.3%), endometrial hyperplasia (18.8%) and adenomyosis (12.5%) were the most common histopathological findings detected in vaginal hysterectomy specimens.
Conclusion: The combination of vaginal hysterectomy and total colpocleisis appears as a safe and efficient approach which does not contribute to the surgery-related morbidity despite the significantly longer operative time.
Related collections
Most cited references29
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Short forms of two condition-specific quality-of-life questionnaires for women with pelvic floor disorders (PFDI-20 and PFIQ-7).
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found