- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Endometrial regenerative cells: A novel stem cell population
Read this article at
Abstract
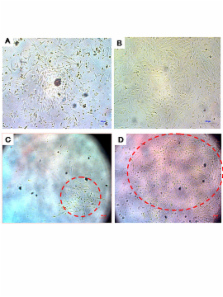
Angiogenesis is a critical component of the proliferative endometrial phase of the menstrual cycle. Thus, we hypothesized that a stem cell-like population exist and can be isolated from menstrual blood. Mononuclear cells collected from the menstrual blood contained a subpopulation of adherent cells which could be maintained in tissue culture for >68 doublings and retained expression of the markers CD9, CD29, CD41a, CD44, CD59, CD73, CD90 and CD105, without karyotypic abnormalities. Proliferative rate of the cells was significantly higher than control umbilical cord derived mesenchymal stem cells, with doubling occurring every 19.4 hours. These cells, which we termed "Endometrial Regenerative Cells" (ERC) were capable of differentiating into 9 lineages: cardiomyocytic, respiratory epithelial, neurocytic, myocytic, endothelial, pancreatic, hepatic, adipocytic, and osteogenic. Additionally, ERC produced MMP3, MMP10, GM-CSF, angiopoietin-2 and PDGF-BB at 10–100,000 fold higher levels than two control cord blood derived mesenchymal stem cell lines. Given the ease of extraction and pluripotency of this cell population, we propose ERC as a novel alternative to current stem cells sources.
Related collections
Most cited references21
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Oocyte generation in adult mammalian ovaries by putative germ cells in bone marrow and peripheral blood.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Isolation and characterization of a stem cell population from adult human liver.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found