- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Trinity of Three-Dimensional (3D) Scaffold, Vibration, and 3D Printing on Cell Culture Application: A Systematic Review and Indicating Future Direction
Read this article at
Abstract
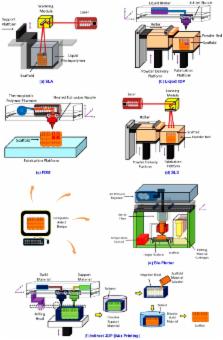
Cell culture and cell scaffold engineering have previously developed in two directions. First can be ‘static into dynamic’, with proven effects that dynamic cultures have benefits over static ones. Researches in this direction have used several mechanical means, like external vibrators or shakers, to approximate the dynamic environments in real tissue, though such approaches could only partly address the issue. Second, can be ‘2D into 3D’, that is, artificially created three-dimensional (3D) passive (also called ‘static’) scaffolds have been utilized for 3D cell culture, helping external culturing conditions mimic real tissue 3D environments in a better way as compared with traditional two-dimensional (2D) culturing. In terms of the fabrication of 3D scaffolds, 3D printing (3DP) has witnessed its high popularity in recent years with ascending applicability, and this tendency might continue to grow along with the rapid development in scaffold engineering. In this review, we first introduce cell culturing, then focus 3D cell culture scaffold, vibration stimulation for dynamic culture, and 3DP technologies fabricating 3D scaffold. Potential interconnection of these realms will be analyzed, as well as the limitations of current 3D scaffold and vibration mechanisms. In the recommendation part, further discussion on future scaffold engineering regarding 3D vibratory scaffold will be addressed, indicating 3DP as a positive bridging technology for future scaffold with integrated and localized vibratory functions.
Related collections
Most cited references95
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Recent advances in bone tissue engineering scaffolds.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Mechanical forces direct stem cell behaviour in development and regeneration
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found