- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
HDAC6 Inhibitors Modulate Lys49 Acetylation and Membrane Localization of β-Catenin in Human iPSC-Derived Neuronal Cells

Read this article at
Abstract
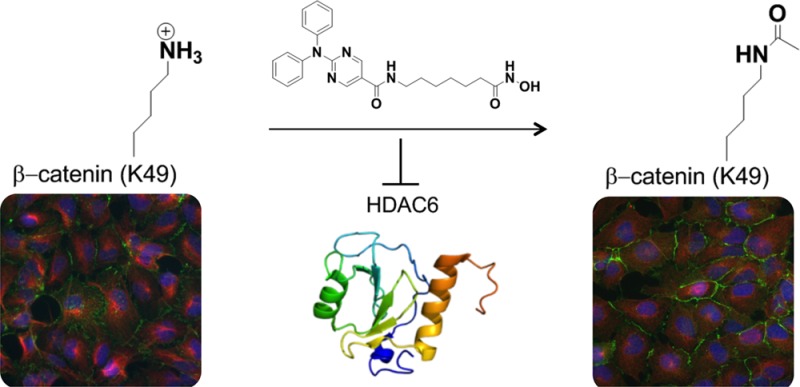
We examined the effects of isoform-specific histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors on β-catenin posttranslational modifications in neural progenitor cells (NPCs) derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs). β-catenin is a multifunctional protein with important roles in the developing and adult central nervous system. Activation of the Wnt pathway results in stabilization and nuclear translocation of β-catenin, resulting in activation of multiple target genes. In addition, β-catenin forms a complex with cadherins at the plasma membrane as part of the adherens junctions. The N-terminus of β-catenin has phosphorylation, ubiquitination, and acetylation sites that regulate its stability and signaling. In the absence of a Wnt signal, Ser33, Ser37, and Thr41 are constitutively phosphorylated by glycogen synthase kinase 3β (GSK3β). β-Catenin phosphorylated at these sites is recognized by β-transducin repeat-containing protein (βTrCP), which results in ubiquitination and degradation by the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. The N-terminal regulatory domain of β-catenin also includes Ser45, a phosphorylation site for Casein Kinase 1α (CK1α) and Lys49, which is acetylated by the acetyltransferase p300/CBP-associated factor (PCAF). The relevance of Lys49 acetylation and Ser45 phosphorylation to the function of β-catenin is an active area of investigation. We find that HDAC6 inhibitors increase Lys49 acetylation and Ser45 phosphorylation but do not affect Ser33, Ser37, and Thr41 phosphorylation. Lys49 acetylation results in decreased ubiquitination of β-catenin in the presence of proteasome inhibition. While increased Lys49 acetylation does not affect total levels of β-catenin, it results in increased membrane localization of β-catenin.
Related collections
Most cited references42
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Proximal events in Wnt signal transduction.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
