- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Correlation of Choroidal Thickness and Volume Measurements with Axial Length and Age Using Swept Source Optical Coherence Tomography and Optical Low-Coherence Reflectometry
Read this article at
Abstract
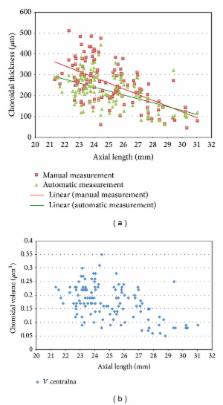
Purpose. To report choroidal thickness and volume in healthy eyes using swept source optical coherence tomography (SS-OCT). Methods. A prospective observational study of 122 patients examined with swept source OCT (DRI-OCT, Topcon, Japan). In each eye, we performed 256 horizontal scans, 12 mm in length and centered on the fovea. We calculated choroidal thickness manually with a built-in caliper and automatically using DRI-OCT mapping software. Choroidal volume was also automatically calculated. We measured axial length with optical low-coherence reflectometry (Lenstar LS 900, Haag-Streit, Switzerland). Results. The choroid has focally increased thickness under the fovea. Choroid was thinnest in the outer nasal quadrant. In stepwise regression analysis, age was estimated as the most significant factor correlating with decreased choroidal thickness ( F = 23.146, P < 0.001) followed by axial length ( F = 4.902, P = 0.03). Refractive error was not statistically significant ( F = 1.16, P = 0.28). Conclusions. SS-OCT is the first commercially available system that can automatically create choroidal thickness and volume maps. Choroidal thickness is increased at the fovea and is thinnest nasally. Age and axial length are critical for the estimation of choroidal thickness and volume. Choroidal measurements derived from SS-OCT images have potential value for objectively documenting disease-related choroidal thickness abnormalities and monitoring progressive changes over time.
Related collections
Most cited references17
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Enhanced depth imaging optical coherence tomography of the choroid in central serous chorioretinopathy.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Enhanced depth imaging spectral-domain optical coherence tomography.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found