- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Comparative Analysis of Chemical Constituents of Moringa oleifera Leaves from China and India by Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography Coupled with Quadrupole-Time-Of-Flight Mass Spectrometry
Read this article at
Abstract
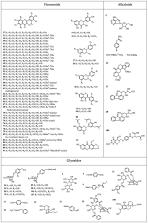
With the aim to discuss the similarities and differences of phytochemicals in Moringa oleifera leaves collected from China (CML) and India (IML) in mind, comparative ultra-performance liquid chromatography coupled with quadrupole-time-of-flight mass spectrometry (UPLC-QTOF-MS) analysis was performed in this study. A screening analysis based on a UNIFI platform was first carried out to discuss the similarities. Next, untargeted metabolomic analysis based on multivariate statistical analysis was performed to discover the differences. As a result, a total of 122 components, containing 118 shared constituents, were characterized from CML and IML. The structure types included flavonoids, alkaloids, glyosides, organic acids and organic acid esters, iridoids, lignans, and steroids, etc. For CML, 121 compounds were characterized; among these, 18 potential biomarkers with higher contents enabled differentiation from IML. For IML, 119 compounds were characterized; among these, 12 potential biomarkers with higher contents enabled differentiation from CML. It could be concluded that both CML and IML are rich in phytochemicals and that CML is similar to IML in the kinds of the compounds it contains, except for the significant differences in the contents of some compounds. This comprehensive phytochemical profile study provides a basis for explaining the effect of different growth environments on secondary metabolites and exists as a reference for further research into or applications of CML in China.
Related collections
Most cited references70

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Moringa Genus: A Review of Phytochemistry and Pharmacology
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Antiproliferation and induction of apoptosis by Moringa oleifera leaf extract on human cancer cells.

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found