- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Collagen V-induced nasal tolerance downregulates pulmonary collagen mRNA gene and TGF-beta expression in experimental systemic sclerosis
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
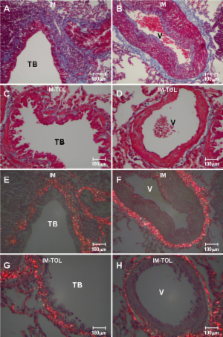
The purpose of this study was to evaluate collagen deposition, mRNA collagen synthesis and TGF-beta expression in the lung tissue in an experimental model of scleroderma after collagen V-induced nasal tolerance.
Methods
Female New Zealand rabbits (N = 12) were immunized with 1 mg/ml of collagen V in Freund's adjuvant (IM). After 150 days, six immunized animals were tolerated by nasal administration of collagen V (25 μg/day) (IM-TOL) daily for 60 days. The collagen content was determined by morphometry, and mRNA expressions of types I, III and V collagen were determined by Real-time PCR. The TGF-beta expression was evaluated by immunostaining and quantified by point counting methods. To statistic analysis ANOVA with Bonferroni test were employed for multiple comparison when appropriate and the level of significance was determined to be p < 0.05.
Results
IM-TOL, when compared to IM, showed significant reduction in total collagen content around the vessels (0.371 ± 0.118 vs. 0.874 ± 0.282, p < 0.001), bronchioles (0.294 ± 0.139 vs. 0.646 ± 0.172, p < 0.001) and in the septal interstitium (0.027 ± 0.014 vs. 0.067 ± 0.039, p = 0.026). The lung tissue of IM-TOL, when compared to IM, showed decreased immunostaining of types I, III and V collagen, reduced mRNA expression of types I (0.10 ± 0.07 vs. 1.0 ± 0.528, p = 0.002) and V (1.12 ± 0.42 vs. 4.74 ± 2.25, p = 0.009) collagen, in addition to decreased TGF-beta expression (p < 0.0001).
Conclusions
Collagen V-induced nasal tolerance in the experimental model of SSc regulated the pulmonary remodeling process, inhibiting collagen deposition and collagen I and V mRNA synthesis. Additionally, it decreased TGF-beta expression, suggesting a promising therapeutic option for scleroderma treatment.
Related collections
Most cited references26
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Oral tolerance: immune mechanisms and the generation of Th3-type TGF-beta-secreting regulatory cells.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Oligoclonal T cell expansion in the skin of patients with systemic sclerosis.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found