- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
C-reactive protein and procalcitonin use in adults in low- and middle-income countries: a narrative review
Read this article at
Abstract
Objectives
C-reactive protein (CRP) and procalcitonin (PCT) are widely used biomarkers in high-income countries. However, evidence for their use in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs) is scant. Because many factors, including rates of endemic disease, comorbidities and genetics, may influence biomarkers’ behaviour, we aimed to review available evidence generated in LMICs.
Methods
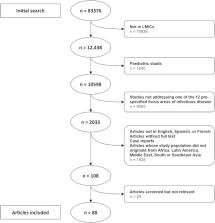
We searched the PubMed database for relevant studies within the last 20 years that originated in regions of interest (Africa, Latin America, Middle East, South Asia or South East Asia), and full-text articles involving diagnosis, prognostication and evaluation of therapeutic response with CRP and/or PCT in adults ( n = 88) were reviewed and categorized in 12 predefined focus areas.
Results
Overall, results were highly heterogeneous, at times conflicting, and often lacking clinically useful cut-off values. However, most studies demonstrated higher levels of CRP/PCT in patients with bacterial versus other infections. HIV and TB patients had consistently higher levels of CRP/PCT versus controls. In addition, higher CRP/PCT levels at baseline and follow-up in HIV, TB, sepsis and respiratory tract infections were associated with poorer prognosis.
Conclusions
Evidence generated from LMIC cohorts suggests that CRP and PCT may have potential to become effective clinical guiding tools particularly in respiratory tract infections, sepsis and HIV/TB. However, more studies are needed to define potential scenarios for use and cost-effectiveness. Consensus across stakeholders regarding target conditions, laboratory standards and cut-off values would support the quality and applicability of future evidence.