- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Correlation of procalcitonin and c-reactive protein levels with pathogen distribution and infection localization in urinary tract infections
Read this article at
Abstract
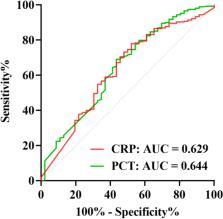
Aimed to explore the relationships between infection localization, bacterial species, and procalcitonin (PCT) and C-reactive protein (CRP) levels in urinary tract infections (UTIs). A retrospective study included 314 UTI hospitalized patients divided into two groups (268 with lower UTI, 46 with upper UTI) in a tertiary care hospital. PCT and CRP were performed. Bacterial isolates were identified using standard microbiological techniques, and statistical analyses were performed to assess associations between infection localization, bacterial species, PCT, and CRP levels. Age and gender showed no significant differences between the lower and upper UTIs. Escherichia coli dominated as the leading UTI pathogen. A positive correlation (r = 0.646, P < 0.001) between PCT and CRP levels was found. The subgroup with ureteritis in the upper UTI category exhibited the highest PCT and CRP levels. PCT and CRP exhibited favorable diagnostic potential in predicting upper UTIs, with AUCs of 0.644 and 0.629, respectively. The optimal cutoff values were 0.21 ng/mL for PCT and 60.77 mg/L for CRP. Sensitivities were 69.03% and 77.99%, while specificities were 56.52% and 47.83%, respectively. E. coli emerged as the predominant bacterium in UTIs. PCT and CRP demonstrated moderate diagnostic efficacy in distinguishing between upper and lower UTIs. Notably, PCT and CRP exhibited enhanced utility in identifying ureteritis.
Related collections
Most cited references22

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Role of C-Reactive Protein at Sites of Inflammation and Infection
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Urinary tract infections: microbial pathogenesis, host–pathogen interactions and new treatment strategies
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found