- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Impact of Patient Engagement on Healthcare Quality: A Scoping Review

Read this article at
Abstract
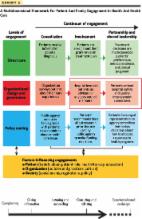
Patient engagement (PE) is a well-known strategy introduced and implemented by pharmaceutical and medical device companies for patient compliance and adherence to treatment protocols during clinical trials and care processes. This can affect a wider range of outcomes such as the quality of treatment decisions and quality of care outcomes. Few studies have paid attention to it. The involvement of patient is one of the crucial stakeholders of health care in their treatment that makes controversial opinions about the potential outcomes of their engagement in various aspects of healthcare. This scoping review was conducted in 2022 to collect the results of PE. The search was performed in the MEDLINE and Web of Sciences databases. The selected documents were categorized and reported by the direct content analysis method. Out of 3974 published documents, 17 articles were selected. Findings are categorized into 4 groups: (1) Health outcome, (2) patient compliance, (3) self-efficiency, and (4) return on investment. PE can improve both treatment outcomes and consequently patient satisfaction and health, as well as the productivity of the service provider. However, increasing self-care and patient adherence are among the positive effects of this engagement on the patient, and return on investment is still a challenge for PE.
Related collections
Most cited references43
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Three approaches to qualitative content analysis.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found