- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
The Minimum Inhibitory Concentration of Antibiotics: Methods, Interpretation, Clinical Relevance
Read this article at
Abstract
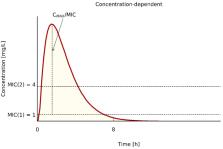
Inefficiency of medical therapies used in order to cure patients with bacterial infections requires not only to actively look for new therapeutic strategies but also to carefully select antibiotics based on variety of parameters, including microbiological. Minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) defines in vitro levels of susceptibility or resistance of specific bacterial strains to applied antibiotic. Reliable assessment of MIC has a significant impact on the choice of a therapeutic strategy, which affects efficiency of an infection therapy. In order to obtain credible MIC, many elements must be considered, such as proper method choice, adherence to labeling rules, and competent interpretation of the results. In this paper, two methods have been discussed: dilution and gradient used for MIC estimation. Factors which affect MIC results along with the interpretation guidelines have been described. Furthermore, opportunities to utilize MIC in clinical practice, with pharmacokinetic /pharmacodynamic parameters taken into consideration, have been investigated. Due to problems related to PK determination in individual patients, statistical estimation of the possibility of achievement of the PK/PD index, based on the Monte Carlo, was discussed. In order to provide comprehensive insights, the possible limitations of MIC, which scientists are aware of, have been outlined.
Related collections
Most cited references90
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Agar and broth dilution methods to determine the minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) of antimicrobial substances.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Determination of minimum inhibitory concentrations.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found