- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
ROS1 Immunohistochemistry Among Major Genotypes of Non—Small-Cell Lung Cancer
Read this article at
Abstract
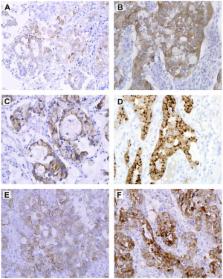
Identification of ROS1 rearrangements in patients with lung cancer allows them to benefit from targeted therapy. We compared immunohistochemistry (IHC) with more cumbersome methods such as fluorescence in situ hybridization and reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction for identification of ROS1 rearrangements in patients with lung adenocarcinoma (n = 33). Our results showed that IHC is a sensitive (100%) and specific (100%) method to identify ROS1 rearrangements in patients with lung cancer.
Background
ROS1 gene fusions cause several cancers by constitutively activating the ROS1 tyrosine kinase receptor. ROS1-targeted inhibitor therapy improves survival in the approximately 1% to 2% of patients with lung adenocarcinoma with ROS1 gene fusions. Although fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) is the standard diagnostic procedure for detecting ROS1 rearrangements, we studied immunohistochemistry (IHC).
Materials and Methods
ROS1 IHC was performed on a selected cohort of 33 lung adenocarcinoma whole tissue specimens with alterations in the EGFR (n = 5), KRAS (n = 5), ERBB2 ( HER2) (n = 3), ROS1 (n = 6), ALK (n = 5), and RET (n = 3) genes and pan-negative (n = 6) detected by reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and FISH.
Results
In the cohort of 33 specimens, both ROS1 gene fusion using RT-PCR and high ROS1 protein expression using IHC were detected in 6 specimens. Of these 6 specimens, 5 were also positive by FISH for ROS1 gene rearrangements. All 27 lung cancer specimens that were negative for ROS1 rearrangements by genetic testing had no to low ROS1 protein expression.
Related collections
Most cited references26
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Global survey of phosphotyrosine signaling identifies oncogenic kinases in lung cancer.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
ROS1 rearrangements define a unique molecular class of lung cancers.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found