- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
New insights on the cardiovascular effects of IGF-1
Read this article at
Abstract
Introduction
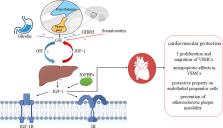
Cardiovascular (CV) disorders are steadily increasing, making them the world’s most prevalent health issue. New research highlights the importance of insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) for maintaining CV health
Methods
We searched PubMed and MEDLINE for English and non-English articles with English abstracts published between 1957 (when the first report on IGF-1 identification was published) and 2022. The top search terms were: IGF-1, cardiovascular disease, IGF-1 receptors, IGF-1 and microRNAs, therapeutic interventions with IGF-1, IGF-1 and diabetes, IGF-1 and cardiovascular disease. The search retrieved original peer-reviewed articles, which were further analyzed, focusing on the role of IGF-1 in pathophysiological conditions. We specifically focused on including the most recent findings published in the past five years.
Results
IGF-1, an anabolic growth factor, regulates cell division, proliferation, and survival. In addition to its well-known growth-promoting and metabolic effects, there is mounting evidence that IGF-1 plays a specialized role in the complex activities that underpin CV function. IGF-1 promotes cardiac development and improves cardiac output, stroke volume, contractility, and ejection fraction. Furthermore, IGF-1 mediates many growth hormones (GH) actions. IGF-1 stimulates contractility and tissue remodeling in humans to improve heart function after myocardial infarction. IGF-1 also improves the lipid profile, lowers insulin levels, increases insulin sensitivity, and promotes glucose metabolism. These findings point to the intriguing medicinal potential of IGF-1. Human studies associate low serum levels of free or total IGF-1 with an increased risk of CV and cerebrovascular illness. Extensive human trials are being conducted to investigate the therapeutic efficacy and outcomes of IGF-1-related therapy.
Discussion
We anticipate the development of novel IGF-1-related therapy with minimal side effects. This review discusses recent findings on the role of IGF-1 in the cardiovascular (CVD) system, including both normal and pathological conditions. We also discuss progress in therapeutic interventions aimed at targeting the IGF axis and provide insights into the epigenetic regulation of IGF-1 mediated by microRNAs.
Related collections
Most cited references228
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The functions of animal microRNAs.
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found