- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Silver Nanoparticles in the Lung: Toxic Effects and Focal Accumulation of Silver in Remote Organs

Read this article at
Abstract
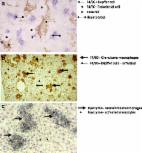
The distribution of silver (Ag) into remote organs secondary to the application of Ag nanoparticles (Ag-NP) to the lung is still incompletely understood and was investigated in the rat with imaging methods. Dose-finding experiments were carried out with 50 nm- or 200 nm-sized polyvinyl pyrrolidine (PVP)-coated Ag-NP using alveolar macrophages in vitro and female rats, which received Ag-NP via intratracheal instillation. In the main study, we administered 37.5–300 µg per rat lung of the more toxic Ag50-PVP and assessed the broncho-alveolar lavage fluid (BALF) for inflammatory cells, total protein and fibronectin after three and 21 days. In parallel, lung tissue was analysed for DNA double-strand breaks and altered cell proliferation. While 75–150 µg Ag50-PVP per rat lung caused a reversible inflammation, 300 µg led to DNA damage, accelerated cell proliferation and progressively increasing numbers of neutrophilic granulocytes. Ag accumulation was significant in homogenates of liver and other peripheral organs upon lung dose of ≥75 µg. Quantitative laser-ablation inductively-coupled plasma mass spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS) combined with enhanced dark field microscopy and autometallography revealed focal accumulations of Ag and/or Ag-NP in sections of peripheral organs: mediastinal lymph nodes contained Ag-NP especially in peripheral macrophages and Ag in argyrophilic fibres. In the kidney, Ag had accumulated within proximal tubuli, while renal filter structures contained no Ag. Discrete localizations were also observed in immune cells of liver and spleen. Overall, the study shows that concentrations of Ag-NP, which elicit a transient inflammation in the rat lung, lead to focal accumulations of Ag in peripheral organs, and this might pose a risk to particular cell populations in remote sites.
Related collections
Most cited references54

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Size-dependent cytotoxicity of silver nanoparticles in human lung cells: the role of cellular uptake, agglomeration and Ag release
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Tissue macrophages: heterogeneity and functions
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found