- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Chitosan as possible inhibitory agents and delivery systems in leukemia
Read this article at
Abstract
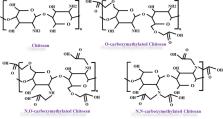
Leukemia is a lethal cancer in which white blood cells undergo proliferation and immature white blood cells are seen in the bloodstream. Without diagnosis and management in early stages, this type of cancer can be fatal. Changes in protooncogenic genes and microRNA genes are the most important factors involved in development of leukemia. At present, leukemia risk factors are not accurately identified, but some studies have pointed out factors that predispose to leukemia. Studies show that in the absence of genetic risk factors, leukemia can be prevented by reducing the exposure to risk factors of leukemia, including smoking, exposure to benzene compounds and high-dose radioactive or ionizing radiation. One of the most important treatments for leukemia is chemotherapy which has devastating side effects. Chemotherapy and medications used during treatment do not have a specific effect and destroy healthy cells besides leukemia cells. Despite the suppressing effect of chemotherapy against leukemia, patients undergoing chemotherapy have poor quality of life. So today, researchers are focusing on finding more safe and effective natural compounds and treatments for cancer, especially leukemia. Chitosan is a valuable natural compound that is biocompatible and non-toxic to healthy cells. Anticancer, antibacterial, antifungal and antioxidant effects are examples of chitosan biopolymer properties. The US Food and Drug Administration has approved the use of this compound in medical treatments and the pharmaceutical industry. In this article, we take a look at the latest advances in the use of chitosan in the treatment and improvement of leukemia.
Related collections
Most cited references235
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Chitin and chitosan: Properties and applications
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found