- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Effects of tyrosol and farnesol on Candida albicans biofilm
Read this article at
Abstract
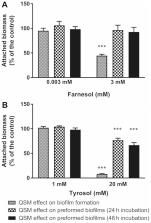
The present in vitro study examined the effects of the quorum-sensing molecules farnesol and tyrosol on the development of Candida albicans biofilm in order to elucidate their role as novel adjuvants in oral hygiene. The investigation was conducted in C. albicans ATCC 10231 and C. albicans isolates from dentures and was performed in flat-bottomed 96-well polystyrene plates. Yeast growth and their capacity to form biofilms were evaluated following 24 and 48 h incubations at 37°C in Sabouraud broth supplemented with 0.001–3 mM farnesol and/or 1–20 mM tyrosol. Yeast growth was assessed by turbidimetry and biofilms were quantitated by crystal violet staining, under aerobic and anaerobic conditions. The viability of the fungal cells was controlled by the culture of planktonic cells and by examination of the biofilms using fluorescence microscopy following staining with fluorescein diacetate and ethidium bromide. Farnesol at 3 mM exerted a stronger action when added at the beginning of biofilm formation (>50% inhibition) than when added to preformed biofilms (<10% inhibition). Similarly, tyrosol at 20 mM had a greater effect on biofilm formation (>80% inhibition) than on preformed biofilms (<40% inhibition). Despite significant reductions in attached biomass, yeast growth varied little in the presence of the investigated molecules, as corroborated by the turbidimetry, culture of supernatants on solid culture medium followed by counting of colony-forming units and viability tests using fluorescence microscopy. At the highest tested concentration, the molecules had a greater effect during the initial phases of biofilm formation. The effect of farnesol during anaerobiosis was not significantly different from that observed during aerobiosis, unlike that of tyrosol during anaerobiosis, which exhibited slightly reduced yeast biofilm inhibition. In conclusion, the present study demonstrated the specific anti-biofilm effect, independent of fungicidal or fungistatic action, of farnesol and tyrosol, as tested in C. albicans ATCC 10231 and 6 strains isolated from dentures. Prior to suggesting the use of these molecules for preventive purposes in oral hygiene, further studies are required in order to clarify the metabolic pathways and cellular mechanisms involved in their antibiofilm effect, as well as the repercussions on the oral microbiome.
Related collections
Most cited references30
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Quorum sensing in the dimorphic fungus Candida albicans is mediated by farnesol.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found