- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Deficient maternal care resulting from immunological stress during pregnancy is associated with a sex-dependent enhancement of conditioned fear in the offspring
Read this article at
Abstract
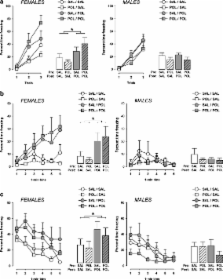
Activation of maternal stress response systems during pregnancy has been associated with altered postpartum maternal care and subsequent abnormalities in the offspring’s brain and behavioral development. It remains unknown, however, whether similar effects may be induced by exposure to immunological stress during pregnancy. The present study was designed to address this issue in a mouse model of prenatal immune activation by the viral mimic polyriboinosinic–polyribocytidilic acid (PolyI:C). Pregnant mice were exposed to PolyI:C-induced immune challenge or sham treatment, and offspring born to PolyI:C- and sham-treated dams were simultaneously cross-fostered to surrogate rearing mothers, which had either experienced inflammatory or vehicle treatment during pregnancy. We evaluated the effects of the maternal immunological manipulation on postpartum maternal behavior, and we assessed the prenatal and postnatal maternal influences on anxiety- and fear-related behavior in the offspring at the peri-adolescent and adult stage of development. We found that PolyI:C treatment during pregnancy led to changes in postpartum maternal behavior in the form of reduced pup licking/grooming and increased nest building activity. Furthermore, the adoption of neonates by surrogate rearing mothers, which had experienced PolyI:C-induced immunological stress during pregnancy, led to enhanced conditioned fear in the peri-adolescent and adult offspring, an effect that was exclusively seen in female but not male subjects. Unconditioned (innate) anxiety-related behavior as assessed in the elevated plus maze and open field explorations tests were not affected by the prenatal and postnatal manipulations. Our results thus highlight that being raised by gestationally immune-challenged surrogate mothers increases the vulnerability for specific forms of fear-related behavioral pathology in later life, and that this association may be mediated by deficits in postpartum maternal care. This may have important implications for the identification and characterization of early-life risk factors involved in the developmental etiology of fear-related neuropsychiatric disorders.
Related collections
Most cited references55
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The adolescent brain and age-related behavioral manifestations.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Maternal care, hippocampal glucocorticoid receptors, and hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal responses to stress.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
