- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Kidney Dysfunction After Traumatic Brain Injury: Pathophysiology and General Management
Read this article at
Abstract
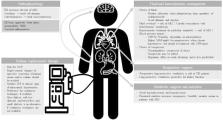
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) remains a major cause of mortality and morbidity, and almost half of these patients are admitted to the intensive care unit. Of those, 10% develop acute kidney injury (AKI) and 2% even need kidney replacement therapy (KRT). Although clinical trials in patients with TBI who have AKI are lacking, some general principles in this population may apply. The present review is an overview on the epidemiology and pathophysiology of AKI in patients with TBI admitted to the intensive care unit who are at risk for or who have developed AKI. A cornerstone in severe TBI management is preventing secondary brain damage, in which reducing the intracranial pressure (ICP) and optimizing the cerebral perfusion pressure (CPP) remain important therapeutic targets. To treat episodes of elevated ICP, osmolar agents such as mannitol and hypertonic saline are frequently administered. Although we are currently awaiting the results of a prospective randomized controlled trial that compares both agents, it is important to realize that both agents have been associated with an increased risk of developing AKI which is probably higher for mannitol compared with hypertonic saline. For the brain, as well as for the kidney, targeting an adequate perfusion pressure is important. Hemodynamic management based on the combined use of intravascular fluids and vasopressors is ideally guided by hemodynamic monitoring. Hypotonic albumin or crystalloid resuscitation solutions may increase the risk of brain edema, and saline-based solutions are frequently used but have a risk of hyperchloremia, which might jeopardize kidney function. In patients at risk, frequent assessment of serum chloride might be advised. Maintenance of an adequate CPP involves the optimization of circulating blood volume, often combined with vasopressor agents. Whether individualized CPP targets based on cerebrovascular autoregulation monitoring are beneficial need to be further investigated. Interestingly, such individualized perfusion targets are also under investigation in patients as a strategy to mitigate the risk for AKI in patients with chronic hypertension. In the small proportion of patients with TBI who need KRT, continuous techniques are advised based on pathophysiology and expert opinion. The need for KRT is associated with a higher risk of intracranial hypertension, especially if osmolar clearance occurs fast, which can even occur in continuous techniques. Precise ICP and CPP monitoring is mandatory, especially at the initiation of KRT.
Related collections
Most cited references97
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Ventilation with lower tidal volumes as compared with traditional tidal volumes for acute lung injury and the acute respiratory distress syndrome. The Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Network.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Guidelines for the Management of Severe Traumatic Brain Injury, Fourth Edition.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
