- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Six-lead electrocardiography compared to single-lead electrocardiography and photoplethysmography of a wrist-worn device for atrial fibrillation detection controlled by premature atrial or ventricular contractions: six is smarter than one
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
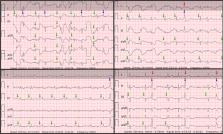
Smartwatches are commonly capable to record a lead-I-like electrocardiogram (ECG) and perform a photoplethysmography (PPG)-based atrial fibrillation (AF) detection. Wearable technologies repeatedly face the challenge of frequent premature beats, particularly in target populations for screening of AF.
Objective
To investigate the potential diagnostic benefit of six-lead ECG compared to single-lead ECG and PPG-based algorithm for AF detection of the wrist-worn device.
Methods and results
From the database of DoubleCheck-AF 249 adults were enrolled in AF group ( n = 121) or control group of SR with frequent premature ventricular (PVCs) or atrial (PACs) contractions ( n = 128). Cardiac rhythm was monitored using a wrist-worn device capable of recording continuous PPG and simultaneous intermittent six-lead standard-limb-like ECG. To display a single-lead ECG, the six-lead ECGs were trimmed to lead-I-like ECGs. Two diagnosis-blinded cardiologists evaluated reference, six-lead and single-lead ECGs as “AF”, “SR”, or “Cannot be concluded”. AF detection based on six-lead ECG, single-lead ECG, and PPG yielded a sensitivity of 99.2%, 95.7%, and 94.2%, respectively. The higher number of premature beats per minute was associated with false positive outcomes of single-lead ECG (18.80 vs. 5.40 beats/min, P < 0.01), six-lead ECG (64.3 vs. 5.8 beats/min, P = 0.018), and PPG-based detector (13.20 vs. 5.60 beats/min, P = 0.05). Single-lead ECG required 3.4 times fewer extrasystoles than six-lead ECG to result in a false positive outcome. In a control subgroup of PACs, the specificity of six-lead ECG, single-lead ECG, and PPG dropped to 95%, 83.8%, and 90%, respectively. The diagnostic value of single-lead ECG (AUC 0.898) was inferior to six-lead ECG (AUC 0.971) and PPG-based detector (AUC 0.921). In a control subgroup of PVCs, the specificity of six-lead ECG, single-lead ECG, and PPG was 100%, 96.4%, and 96.6%, respectively. The diagnostic value of single-lead ECG (AUC 0.961) was inferior to six-lead ECG (AUC 0.996) and non-inferior to PPG-based detector (AUC 0.954).
Conclusions
A six-lead wearable-recorded ECG demonstrated the superior diagnostic value of AF detection compared to a single-lead ECG and PPG-based AF detection. The risk of type I error due to the widespread use of smartwatch-enabled single-lead ECGs in populations with frequent premature beats is significant.
Related collections
Most cited references24
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Global epidemiology of atrial fibrillation: An increasing epidemic and public health challenge
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found