- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Are Differences in Physical Activity across Socioeconomic Groups Associated with Choice of Physical Activity Variables to Report?
Read this article at
Abstract
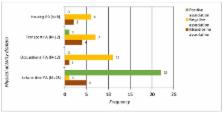
Despite being challenged in recent years, the hypothesis that individuals of higher socioeconomic status (SES) are more physically active than their lower SES counterparts is generally considered a fact. Recent reviews, however, have suggested that differences across groups might be related to which physical activity (PA) domains have been investigated. In the present review, searches for relevant studies were performed in the MEDLINE, ISI Web of Knowledge and SPORTDiscus databases. Search terms included “socioeconomic”, “socio-economic”, “socio economic” and “social class” to meet all variations of the variable “socioeconomic status” in combination with the term “physical activity”. Studies were included when applying the dimensions of intensity, frequency, type/mode, and duration in measuring PA. Fifty-six studies were included and were subsequently split into four PA domains: transport PA (TPA), occupational PA (OPA), housing PA (HPA) and leisure time PA (LTPA). It turned out that the positive relationship held only for LTPA, whereas the relationship was non-existent or even opposite for all other domains. It is concluded that the assumed positive relationship between SES and PA is mainly a relationship between LTPA and SES. It is further suggested that the PA domain should always be considered when studying said relationships.
Related collections
Most cited references71
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Socioeconomic status differences in recreational physical activity levels and real and perceived access to a supportive physical environment.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found