- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Potential for enriching next-generation health-promoting gut bacteria through prebiotics and other dietary components
Read this article at
ABSTRACT
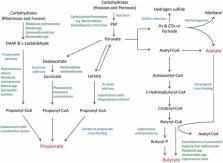
The human intestinal commensal microbiota and associated metabolic products have long been regarded as contributors to host health. As the identity and activities of the various members of this community have become clearer, newly identified health-associated bacteria, such as Faecalibacterium prausnitzii, Akkermansia muciniphila, Ruminococcus bromii and Roseburia species, have emerged. Notably, the abundance of many of these bacteria is inversely correlated to several disease states. While technological and regulatory hurdles may limit the use of strains from these taxa as probiotics, it should be possible to utilize prebiotics and other dietary components to selectively enhance their growth in situ. Dietary components of potential relevance include well-established prebiotics, such as galacto-oligosaccharides, fructo-oligosaccharides and inulin, while other putative prebiotics, such as other oligosaccharides, polyphenols, resistant starch, algae and seaweed as well as host gut metabolites such as lactate and acetate, may also be applied with the aim of selectively and/or differentially affecting the beneficial bacterial community within the gastrointestinal environment. The present review provides an overview of the dietary components that could be applied in this manner.
Related collections
Most cited references62

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Intestinal Short Chain Fatty Acids and their Link with Diet and Human Health
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Benefits of polyphenols on gut microbiota and implications in human health.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found