- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
O-GlcNAcylation of TAB1 modulates TAK1-mediated cytokine release
Read this article at
Abstract
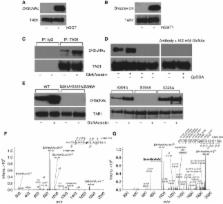
Transforming growth factor (TGF)-β-activated kinase 1 (TAK1) is a key serine/threonine protein kinase that mediates signals transduced by pro-inflammatory cytokines such as transforming growth factor-β, tumour necrosis factor (TNF), interleukin-1 (IL-1) and wnt family ligands. TAK1 is found in complex with binding partners TAB1–3, phosphorylation and ubiquitination of which has been found to regulate TAK1 activity. In this study, we show that TAB1 is modified with N-acetylglucosamine ( O-GlcNAc) on a single site, Ser395. With the help of a novel O-GlcNAc site-specific antibody, we demonstrate that O-GlcNAcylation of TAB1 is induced by IL-1 and osmotic stress, known inducers of the TAK1 signalling cascade. By reintroducing wild-type or an O-GlcNAc-deficient mutant TAB1 (S395A) into Tab1 −/− mouse embryonic fibroblasts, we determined that O-GlcNAcylation of TAB1 is required for full TAK1 activation upon stimulation with IL-1/osmotic stress, for downstream activation of nuclear factor κB and finally production of IL-6 and TNFα. This is one of the first examples of a single O-GlcNAc site on a signalling protein modulating a key innate immunity signalling pathway.
Related collections
Most cited references44
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Missing pieces in the NF-kappaB puzzle.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Identification of a member of the MAPKKK family as a potential mediator of TGF-beta signal transduction.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found