- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Post-Translational Modifications of the TAK1-TAB Complex
Read this article at
Abstract
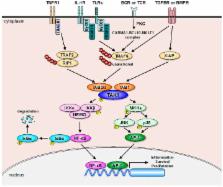
Transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β)-activated kinase 1 (TAK1) is a member of the mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase (MAPKKK) family that is activated by growth factors and cytokines such as TGF-β, IL-1β, and TNF-α, and mediates a wide range of biological processes through activation of the nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) and the mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase signaling pathways. It is well established that activation status of TAK1 is tightly regulated by forming a complex with its binding partners, TAK1-binding proteins (TAB1, TAB2, and TAB3). Interestingly, recent evidence indicates the importance of post-translational modifications (PTMs) of TAK1 and TABs in the regulation of TAK1 activation. To date, a number of PTMs of TAK1 and TABs have been revealed, and these PTMs appear to fine-tune and coordinate TAK1 activities depending on the cellular context. This review therefore focuses on recent advances in the understanding of the PTMs of the TAK1-TAB complex.
Related collections
Most cited references99
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Activation of the IkappaB kinase complex by TRAF6 requires a dimeric ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme complex and a unique polyubiquitin chain.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
A role for ubiquitin in selective autophagy.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found